Garmin Is The Latest Victim of Ransomware Attacks


- Who was behind the Garmin ransomware attack?
- What did Garmin say?
- Ransomware explained
- Best way to prevent ransomware attacks
A 2015 HP study uncovered that smartwatches have serious cybersecurity weaknesses. The company assessed ten of these wearable devices and found that each one had significant vulnerabilities, mostly thanks to a complacent and indifferent attitude from manufacturers.
As a result, smartwatches and wearable technology, in general, were subject to plenty of cyberattacks. The most recent one targeted Garmin, a US fitness-tracker and GPS company. According to several sources, the smartwatch maker was hit by a ransomware attack called WastedLocker, which was reportedly developed by Evil Corp.
The US government sanctioned the Russian hacking group back in December, prohibiting any American company from paying ransoms. Perhaps that’s why Garmin avoided mentioning any ransom demands and only confirmed it was a victim of cybercrime.
The Garmin Attack
Garmin is a US company that specializes in GPS technology for the automotive, marine, aviation, and sports sectors. It also manufactures wearable technology like smartwatches, making it a competitor to Fitbit, Apple, and others.
But Garmin suffered a security breach in July that forced it to shut down its website, apps, and call centers. Customers started reporting that they were unable to use services like Garmin Connect and flyGarmin. The company said that it opened an investigation into the matter before confirming on Monday that the cause of the outage was a cyberattack.
The latter prevented the smartwatch manufacturer from accessing online chats or receiving calls and emails. Moreover, athletes were no longer able to track data like heart rate, location, and mileage. As for flyGarmin, pilots couldn’t download aircraft navigational data, which is a Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) requirement before flights.
In a brief statement, Garmin said that the hack encrypted some of its systems, with no indication of any user data breach. It added everything should return to normal in the coming days but warned there could be an accumulation of user data to process.
“We have no indication that any customer data, including payment information from Garmin Pay, was accessed, lost or stolen.”
Garmin
Why Is Garmin Quiet?
Despite stating that the attack encrypted certain systems, Garmin avoided any references to ransoms. But according to multiple sources and company employees, the malicious software was ransomware called WastedLocker. The latter is supposedly a product of Evil Corp, a Russian hacking group that got on the US government’s sanctions list last December.
As a result, it’s illegal for any American corporation to pay ransoms for the return of files and data. So the reason behind Garmin not disclosing the nature of the attack was due to fears of a backlash from the authorities. Yet, after systems were back online earlier this week, experts are confident that Garmin caved to the hackers’ demands. Some reports even suggested that cybercriminals asked for $10 million.
WastedLocker first came to light in a report by anti-malware provider Malwarebytes. It is a new ransomware that specifically targets organizations. During the first steps of the attack, WastedLocker examines and analyses the network’s security system to facilitate further breaches. Then, it proceeds to encrypt your files and leave a ransom note.
The ransomware’s name comes from the file it attacks as it adds the extension “wasted” at the end of the filename. For every file they encrypt, the attackers create a separate one containing the ransom note. They give it the same name as the encrypted file, with the addition of “_info.”
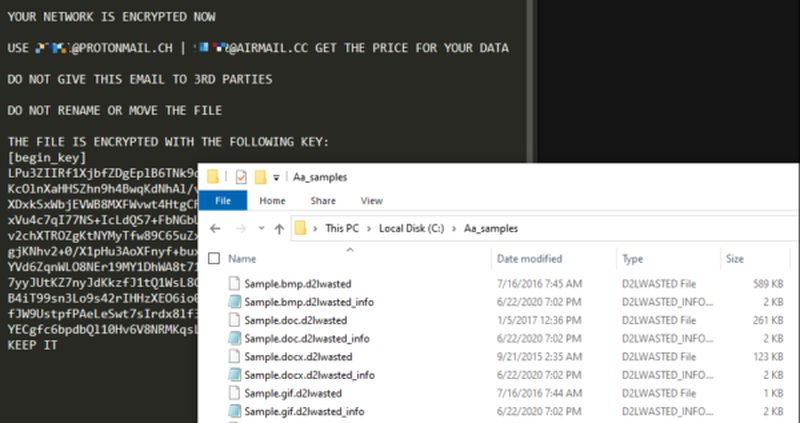

Hackers who use WastedLocker demand lucrative payouts ranging between $500,000 and $10 million in Bitcoin. It targets every file and backup so that companies have no choice but to pay to get the decryption key. And while other attackers use ransomware to steal data and auction it on the Dark Web, Evil Corp has never engaged in such actions.
What Is Ransomware?
Ransomware is a type of malicious software that, once past your security system, infiltrates and encrypts your files. It keeps your data hostage until you pay a ransom in the form of Bitcoin. Only then will the attackers give you the decryption key. The most common way to breach your device is through phishing scams.
Cybercriminals send emails in bulk posing as legitimate employees and asking you to make account settings by clicking a link. The latter is actually malicious and allows hackers to install malware on your device. Other methods are more aggressive and don’t require any action from victims. For example, WannaCry and NotPetya infect networks by exploiting system weaknesses.
Furthermore, holding files to ransom isn’t the only trick in the book. Attackers sometimes impersonate law enforcement officers after breaking into your system. They’ll claim that you entered illegal websites or downloaded copyrighted material and shot down your computer. The only way to get it up and running again is by paying a fine.
Other hackers use extortionware, or doxware, which, as the names suggest, involve blackmail and extortion. Perpetrators get their hands on intimate files like photos, emails, or documents and threaten to release them all over the web unless you pay what they ask.
How to Prevent Ransomware Attacks
Ransomware was the talk of the town in the cybercrime world in 2017. It helped criminals acquire Bitcoins, which were extremely popular and soaring at the time. But when cryptojacking malware came into the frame, ransomware stocks plummeted among hackers. Cryptojacking allowed them to mine Bitcoin by stealing your computer’s resources and computing power without your knowledge.
But despite its demise, ransomware is still very much out there. In fact, the number of attacks more than doubled in 2019. Therefore, you must stay vigilant as the best way to prevent ransomware-related attacks is by taking precautionary measures. That includes:
- The first step starts with you. Please make sure the links or files you receive via email are legitimate before opening them. If you encounter suspicious messages, report them to your company’s network administrator and delete them.
- Always back up important data and files and store them on a separate hard drive that hackers can’t access.
- Regularly update your operating system to mend any potential vulnerability or weakness.
- Download reputable antivirus software that can detect and deter malware. Moreover, you must update your antivirus on a regular basis to catch new viruses and malware.
- Install a premium VPN service with military-grade encryption to prevent third parties from monitoring your online activities.
What to Make of the Garmin Ransomware Attack?
The recent attack on Garmin proves that no matter how big the company, it can still fall victim to cybercrime. It is just the latest in a series of hackings that continue to target large corporations. That is why it’s crucial to stay on your toes whenever you go online and double-check everything before opening or clicking links and files.
Moreover, we advise you to use PREMIUM cybersecurity tools like antiviruses and VPNs, even if they are a bit expensive. It’s still better and cheaper than paying a ransom to get your data back from a criminal.
Do you think ransomware attacks will go n fashion again? Let us know below.



