Grand Theft Data: How Hackers Can Steal Your Info


- Different ways hackers can steal your data
- Major data breaches
- Data theft - facts and figures
- Why it's crucial to protect your online identity
- How to protect your sensitive data
- Governments take action
Data theft is the act of illegally obtaining someone’s personal information without their consent. And due to the faster dissemination of data through the internet, it’s becoming more frequent. According to the Identity Theft Resource Center (ITRC), 2018 witnessed 1,244 reported breaches.
The number itself is 23% less than the incidents that occurred in 2017. However, the number of exposed sensitive data increased by 126%, which translates to 446.5 million records. An additional 1.68 billion non-sensitive records were compromised as well.
So as you can see, all the statistics point to one thing: Breaches and data theft are here to stay. But how exactly can your private information get stolen so easily?
Content Overview
- How Hackers Can Obtain Your Sensitive Data
- High-profile Data Breaches
- Data Breaches – Stats and Figures
- The Importance of Identity Protection
- How to Determine if Your Data Got Stolen
- How to Secure Your Personal Data
- Governments’ Role in Increasing Online Security, Privacy
- Conclusion
How Hackers Can Obtain Your Sensitive Data
In this modern age, most of our interactions, activities, and even financial transactions take place over the Internet. And while this has rendered them a lot simpler and faster, it also put our data under significant risk. Cybercriminals can now steal our personal records using numerous ways, including:
Malware
Malware is essentially any malicious form of software designed to access or damage a computer system illegally, often without the user’s knowledge. Here are the most common forms of malware that a hacker can use to steal your private information:
Botnets
Botnets are networks of computer systems that have been infected with malware, often remotely controlled by hackers to launch cyberattacks or make financial gains.
If botnets manage to infiltrate your device, they’ll be able to communicate and receive instructions from the “command” computer. The latter can be located anywhere in the world, making it hard to track down. Even worse, modern botnets can self-propagate and transmit themselves to nearby breachable devices.
Some forms of botnets can obtain personal data from the device they infect, without the user’s knowledge. Here are the most common botnets that hackers use: C&C (Command & Control), Telnet, IRC, P2P.
Spyware
Spyware is another unwanted software that hackers use to infect your devices and steal your sensitive data. It can record your private information and immediately relay it to third parties. Hackers, advertisers, data firms, or any other establishment will collect your info.
Cybercriminals use your data to monetize your internet usage data, find private bank account information, or even steal your personal identity. That’s because spyware tracks your login details and monitors your sensitive information.
The ones that are most likely to infiltrate your device are trojans, adware, tracking cookies, and system monitors.
Proxy Servers
Most free proxy servers don’t have an HTTPS connection, which poses a significant threat to your security. HTTPS protocols secure the communication between two systems by encrypting and decrypting the page requests of users. Meanwhile, HTTP protocols do not encrypt your connection to the server, which exposes all your data.
Cookie theft is another way to steal your data. In case you don’t know, cookies store your website data to make your future visits more convenient. When you’re in a free proxy server, however, there’s a possibility that the owner of that server can steal your cookies and impersonate you online using your information.
Finally, proxy servers can accidentally infect your device with malware. That’s because free proxy server owners rely on ads for revenue. They put in advertisements within the site and hope that users will click on them. Unfortunately, scammers can take advantage of this if the owner doesn’t filter out malicious ads.
Phishing
Advanced cybercriminals will try to impersonate trusted or reputable organizations like banks or government institutions. After establishing themselves as a legitimate entity, they will ask for your credentials or infect your device with malware using emails, attachments, or links.
Never click on something you receive from unknown senders or open suspicious-looking emails. You’ll sense trouble if something feels out of the blue (i.e., Apple sending you an email asking for your credentials) or too good to be true (Someone congratulating you for winning a large amount of money.)
Device Theft
Data theft doesn’t have to be remote or over the Internet. There’s also a high possibility of physical stealing in case someone grabs hold of your smartphone, laptop, or tablet.
If your device has a weak password, or worse, no password at all, criminals can easily access your data. Therefore, keep your phone, tablet, or laptop near you at all times and never leave them unattended.
High-profile Data Breaches
As you may know, the majority of data thefts occur when large organizations suffer a breach. Even the institutions we assumed had the most extensive security measures have fallen victims of these attacks. Here are the most notable data breaches in the military, financial, and education sector from 2004 until today.
UK Military Contractor
According to NCC Group researchers, a China-linked cyberespionage group called APT15 infiltrated a UK government contractor’s computer systems. APT15 deployed three backdoors, RoyalCli, RoyalDNS, and BS2005, to collect data about the UK’s military technology.
The attack took place from May 2016 till late 2017 before it was detected, and infected over 30 contractor controlled hosts.
“The group also used keyloggers and their own .NET tool to enumerate folders and dump data from Microsoft Exchange mailboxes.”
NCC Group
Accountancy Firm Deloitte
An advanced and complicated cyber attack managed to hack Deloitte and compromise many confidential plans and high-profile emails. The breach took place back in November 2016, but the “Big Four” accounting firm only discovered it half a year later.
Cybercriminals accessed the firm’s global email server using an “administrator’s account” that, in theory, gave them privileged, unrestricted access.
US OPM – Federal Agency
Hackers accessed millions of Office of Personnel Management (OPM) files in an attack that began in November 2013. That hack exposed sensitive data of federal employees and contractors, as well as their friends and families.
“It’s a treasure trove of information about everybody who has worked for, tried to work for, or works for the United States government.”
James B. Comey, former FBI Director
JP Morgan Chase & Co.
The attack on JP Morgan Chase, a major investment bank and financial services firm, affected the accounts of 76 million households and 7 million businesses. Hackers got their hands on sensitive information that goes beyond client names, phone numbers, addresses, and email addresses.
They also obtained a list of the applications and programs that run on JPMorgan’s computers.
The University of Maryland
The University of Maryland data breach infiltrated over 300,000 records of students, faculty, and staff. Luckily, no medical, academic, or financial information was exposed. However, the names, ID numbers, social security numbers, and birth dates were stolen.
The attack featured data on anyone who had an ID for Maryland’s College Park and Shady Grove campuses since 1998.
University of Greenwich
A serious data breach hit the University of Greenwich in 2016, compromising more than 20,000 email accounts. The attack, which was reportedly carried out by a former student, exposed data like names, addresses, phone numbers, and medical info.
Hackers discovered a vulnerability in an unsecured microsite built back in 2004. It resulted in a £120,000 fine for the university as it failed to shut down or secure the server.
What The Statistics Show
ITRC’s latest annual report reveals that the exposure of private records is increasing at an alarming rate. And while the number of successful data breaches saw a slight decline in 2018, exposed personal information remains at an all-time high.
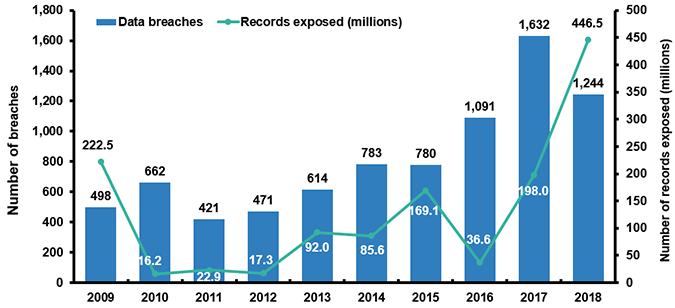

The Consumer Sentinel Network from the Federal Trade Commission also released a report about the most vulnerable states to cybercrime. Here are the number of victims in 2018 by state:
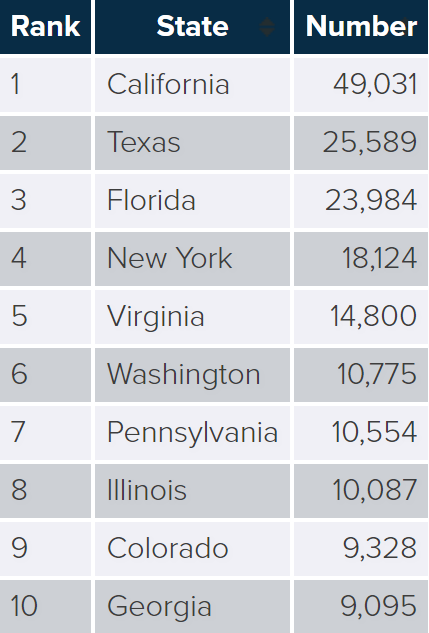

Over the last three years, the number of fraud and identity theft complaints remains high despite the government’s implementation of new cybersecurity policies. It means that cybercriminals are adapting to these new security measures.
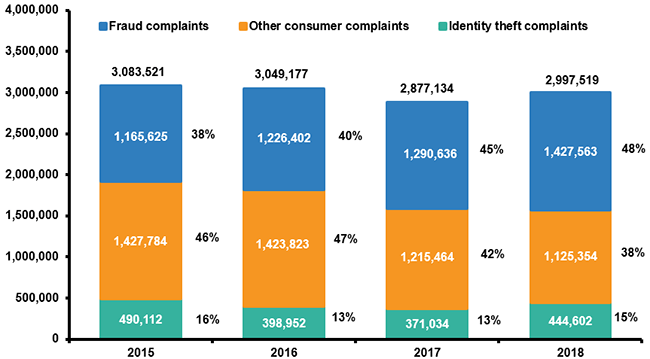

According to the Consumer Sentinel Network, the main source of identity fraud is from new credit card accounts. Cybercriminals open new files posing as their victims. Javelin Strategy’s report found that it has resulted in a loss of $3.4 billion in 2018 and $3 billion in 2017.
While credit cards remain the main focus for new account fraud, other targets include student loans, mortgages, and car loans.
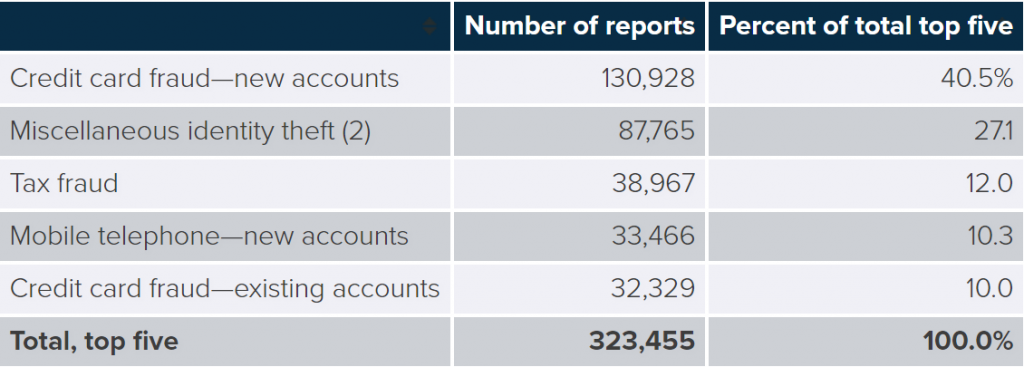

The report also shows that the number of mobile account takeovers has almost doubled in 2018 (679,000) compared to the previous year (380,000). Overall, all account takeovers resulted in more than $3 billion in losses. Employing a fraud alert system is one way of keeping your account secure.
Moreover, Javelin Strategy stated that active social media members are subject to fall victim of fraud because of their high exposure. Regular Facebook, Snapchat, and Instagram users are 46% more likely to face fraud than inactive people.
Whether you’re using online databases for business or pleasure, Always proceed with extra caution. In other words, never give away your sensitive data unless you’re certain the website is safe and secure.
The Importance Of Online Privacy And Identity Protection
In this age of likes, shares, tweets, snaps, and hashtags, online privacy almost seems non-existent. We’re sharing almost every aspect of our lives on social media more than ever before. So what’s the big deal about online privacy if we’re freely revealing our personal information?
Cybercriminals would drool over your financial or personal data. They can use it to steal your identity and go on a spending spree, and you’ll end up paying the bill. That’s because they’ll access all your banking details and obtain loans and credit cards in your name. In other words, it’s your credit rating taking the hit.
Your identity is precious. The ability to prove that you are who you say you are is crucial to all your daily activities. You need it to request loans, get a new passport, or apply for a job. If your identity is stolen, most of your everyday transactions will be compromised.
Furthermore, your reputation, both professionally and privately, will be damaged. That is why you need to protect your online private information by using the best cybersecurity tools, including premium VPNs.
Find Out If Someone Is Using Your Personal Data
The World Wide Web is full of malicious websites and dubious links. And since most cybercrimes take place without the knowledge of users, there’s always a possibility that someone might be using your personal information for illegal purposes.
So if you wish to know whether you’re a fraud victim or not, here’s what you have to do:
Use a Typical Search Engine
The easiest way to find out if someone has stolen your name, email, or other personal data is by a simple Google search. However, the odds are that you will get a lot of unrelated information or people who have the same name as yours.
A quick search is still useful if you see any top hits when you type in your contact information. If you want to dig deeper, you can search the most popular data collection sites like the one below.
Specialized Online Services
Here are some sites that have a database of personal information circulating on the internet:
- BeenVerified
- DOBSearch
- PeopleFinders
- Intelius
- Spoke
- WhitePages
- PeekYou
- Spokeo
- LexisNexis
Can I Delete My Data From These Services?
There are dozens of data aggregators out there, so you can’t fully erase all your public online records. However, you still put a significant dent by making them a little harder to find.
Fortunately, most of these data collectors will remove your information upon your request. Most of their sites have instructions for opting out, and you can find them on pages like Privacy Rights Clearinghouse and UnlistMy.Info.
If you submit a data removal request, and the service fails to comply, you can lodge a formal complaint to the Federal Trade Commission. Moreover, You can contact government bodies and political groups and encourage them to lobby for helpful cybersecurity policy changes that will make these data collecting practices illegal.
The Comprehensive Guide To Securing Your Personal Data
The best way to go about the Internet and its countless risks is to take precautionary measures and secure your data.
Create Backups
The first step to secure your data is creating a backup to your private information. That way, you won’t lose any of it if you lose your device or someone steals it. Create a backup on another device like a separate external hard drive to make it easier for you to replace your lost information.
Encrypt Your Data
Most steer clear whenever they hear the words “data encryption” because it sounds complicated. But you don’t have to be an expert or a tech-savvy user to encrypt your data.
There are plenty of available tools you can use to cipher your sensitive files and emails. For example, you can use the open-source plug-in called GPG (for Apple mail) to encrypt, verify, sign, and decrypt all your emails through the OpenPGP standard.
To protect your files, you can use FileVault, another apple program that automatically encodes your computer’s hard drive. If you’re running on Microsoft Windows devices also have similar programs.
This type of software will regularly scramble all your data. However, it won’t keep you safe from government authorities, because they can still demand your encryption key through the Regulation of Investigatory Powers Act of 2000.
A Variety of Alert Services
If your credit card company or bank offers alert services, you will receive emails or text messages whenever you complete a transaction. That makes it easy to spot and cancel any unauthorized activities.
You can also call Experian, TransUnion, or Equifax (top credit bureaus) and ask for a fraud alert. As a result, you are immediately notified in case of any suspicious activity.
Password Usage
Never share your password with anyone unless you absolutely trust them. An Experian survey revealed that 33% of all adults admitted to sharing account passwords and names with other people.
Another good tip is to avoid opting for the “remember password” option in your browsers. This is a dangerous practice because it leaves your online accounts vulnerable in case your device gets stolen.
To put it simply, use strong and secure passwords that are hard to crack. You can check your passcode’s strength with this tool or utilize a password generator to create one.
Secure Your Wireless Network
For private individuals or business owners, I recommend that you secure your private wireless network using a password. This will prevent any unauthorized individual from using your servers.
It’s also wise to encrypt it and hide it. You can conceal Wi-Fi networks by setting up your router in a way that doesn’t openly broadcast its name, otherwise known as SSID or Service Set Identifier.
Here are a few other ways you can secure your private network, according to the Federal Trade Commission.
VPN Usage
Symantec’s 2017 survey showed that 75% of all consumers don’t use VPNs to secure their Wi-Fi connections. They also note that 87% of these consumers leave their private information exposed when they access their emails, online bank accounts, and financial information.
A virtual private network, better known as a VPN, can help secure your sensitive data by encrypting it and spoofing your online location. While VPNs do have regular fees that you need to pay, they will secure your online transactions.
Anti-Malware Services
It seems that the battle between malware and cybersecurity tools is endless. This malicious software hides within seemingly harmless files and silently collects your data and harms your device without your knowledge. By employing the services of anti-malware providers, you are adding an extra layer of security for your data.
Use Firewalls
Firewalls are another form of protection you can use since they help in blocking any dangerous program from infiltrating your system. Many software companies will offer firewall protection, but those that are built-in, also known as hardware-based firewalls, provide better security.
Install Operating System Updates
While many consider them a pain in the neck and a waste of time, system updates are necessary because they contain the latest security patches to combat recent threats. You can simply opt to make updates automatically if you find manual updating too tedious.
Disable File and Media Sharing
If you have multiple devices connected to your private network, allowing file-sharing might be convenient. However, try as much as possible not to make files public unless it’s completely necessary. Keep some of your folders private, especially those that contain sensitive information.
Enable Remote Location and Device-wiping
In the unfortunate event of losing your device, use tracking apps to see where it is. Some apps will also enable you to remove any sensitive data remotely in case it falls in the hands of a criminal.
Report to the Authorities
According to one of FTC’s reports, 13% of the people who reported identity theft didn’t want police reports taken. By not reporting to the authorities, more people will become victims of these cybercriminals.


Governments Are Starting To Take Action
Due to the increasing security risks to our personal information, many state legislatures are demanding businesses to take extra safety measures when it comes to private data.
Almost half of the US states created laws that directly address the practices of the private sector regarding data security. A majority of these laws require every business to maintain security practices and procedures that will protect user information from any unauthorized access.
In relation to this, most states began implementing data disposal laws, which require entities to destroy any personal information to make them indecipherable.
There are also other federal statutes that specifically aim to increase the security of financial, medical, and social information that business owners collect. For a more comprehensive list, check NCSL’s List of Data Security Laws to see their functions and where they’re enacted.
Data Theft and How to Prevent It – The Wrap Up
Businesses are becoming more and more dependent on compiling our personal data in their databases as a part of their normal operations. We are even sharing our personal info, as we live in an age where social media is prevalent in our society.
Therefore, we are exposed to numerous violations of privacy. Even major institutions and establishments are subject cyber-attacks and data breaches.
With that in mind, you must protect your sensitive information from any outside attack. And the best way to do that is by listening to cybersecurity experts and apply their guide to secure your personal data.
Have you ever been a victim of identity fraud or other data breaches? Share your experience below.



