What is TOR – The Onion Browser Explained


- How Tor works
- Tor with VPN - extra privacy
- Disadvantages of using Tor
- Easy steps to install and use Tor
As cyberattacks and data monitoring continue to grab headlines, online privacy is becoming a precious commodity. Users have access to a variety of tools to maintain their Internet anonymity. The Tor Network, or Tor, is one of the most reliable and publicly available methods to privately browse the Internet or connect to services online.
It started as a project by the US Navy in the mid-1990s, then developed into a free and open-source application for enabling anonymous communications. The two pillars on which the Tor network stands are data encryption and traffic rerouting through a series of machines called network nodes.
Tor can work as a standalone solution or in conjunction with a virtual private network (VPN) service. Volunteers operate worldwide servers to grant you anonymity using The Onion Router. Now, Tor’s concept is similar to that of VPNs as both services use virtual tunnels to connect users. However, there are some noticeable differences between the two.
How Tor Actually Works?
Just like a VPN, the Tor router connects you to a website, online service, or a remote machine through a virtual tunnel.
Standard VPN services reroute your traffic through one of their servers. Some brands offer double VPN, a feature that encrypts and redirects your connection twice, but it is not an option that is automatically enabled. Meanwhile, the Tor network channels your traffic through at least three nodes for extra privacy and security.
Instead of using regular web browsers like Google Chrome or Mozilla Firefox, users shift to the privacy-oriented Tor browser. The latter will route your traffic through the Onion network where your data gets encrypted. Your Tor client builds a chain of at least three secure and random servers called nodes. Your connection travels through each one before reaching its destination.
Furthermore, Tor introduces a new encryption key at each node or network hop. As a result, each node can only know where your traffic came from and where it’s going. In other words, the random nodes cannot track your entire traffic.
Working Tor Connection between Two Users
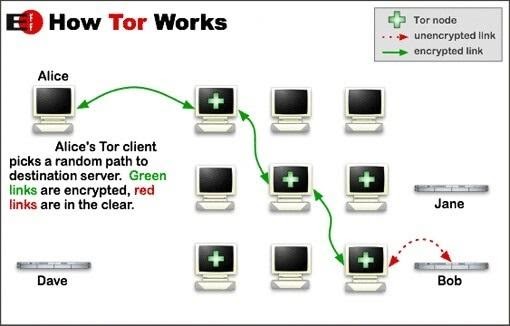

As the image above explains, Tor will encrypt your traffic as it goes through the first random node. The latter will then re-encrypt it and pass it to node number two, where it gets different encryption before traveling to the third node. Next, your connection will exit from the Tor network unencrypted as it reaches its destination.
You’ll also receive data in the same manner, meaning no one can monitor or trace your online activities.
Furthermore, Tor will encrypt your IP address and that of each node. The only IP address your web destination will see is that of the final node, which is also known as the exit node. Therefore, websites and online services won’t be able to trace requests back to you.
Is Tor Really Anonymous?
As the Tor creators openly admit, The Onion Router cannot solve all online privacy problems. It deletes some information about your computer configuration that other browsers share with the destination server. But there are still methods to uncover your identity.
How Tor and HTTPS Protect You
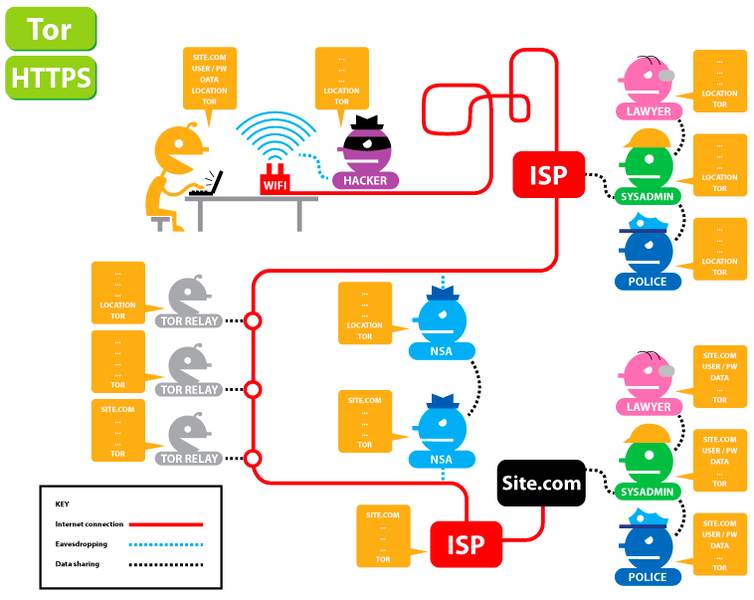
The Tor network protects you against traffic analysis but it cannot protect you against end-to-end timing attacks. Third parties like the authorities, hackers, and Internet service providers can still spot a bit of your sensitive data. Your ISP, for example, will know that you’re using a Tor browser and the websites you visit.
Moreover, The Onion Router won’t do you much good if hackers directly target your device or Wi-Fi connection. As for government agencies, they can still tap your Internet traffic and acquire some sensitive data. As the image below shows, snoopers can still monitor part of your connection even if you’re using a Tor browser.
The illustration also highlights the importance of https connections, which offer SSL encryption. Therefore, make sure the websites you visit have https at the beginning of their URLs and padlock next to it. Otherwise, prying eyes will be able to view your passwords.
Now, the Tor network plus https connections are sufficient for much anonymity. Only advanced attacks can expose your online activities and sensitive data, so don’t worry too much about that. However, for extra security, you can use a virtual private network.

Tor + VPN = Extra Privacy
VPNs route your traffic through a network of their own servers instead of using those of your ISP. They allow you to choose the server you want then send your connection through an encrypted tunnel so that no one can monitor your online activities. You’ll also get a different IP address that matches your server’s location.
In other words, VPNs hide your actual location and make you appear to be elsewhere, all while maintaining your privacy through encryption. Reputable VPN services also don’t keep records of your sensitive data. That includes your IP address (actual and virtual), browsing history, and the websites you visit.
Furthermore, you’ll be able to bypass Internet geo-restrictions and gain more online freedom.
So as you can see, you’ll significantly raise your anonymity levels when you use both the Tor network and a VPN. However, it’s crucial that you install a premium VPN service with top-tier features.

Disadvantages of Using Tor
As we mentioned above, the Tor network gives you anonymous web browsing by encrypting your traffic three times before it reaches its target destination.
That comes at a price, though, as Tor connections are markedly slower than their regular counterparts. Your traffic passes through at least three nodes before reaching its destination, then goes via a similar path to reach your device. As a result, this process slows down your connection.
The speed drop probably won’t bother you if you’re browsing through news websites or social media platforms. However, you might notice it when streaming videos, for example.
Otherwise, it is perfectly legal to use the Tor network and browser in most countries. Nonetheless, nations like Bahrain, Iran, Russia, Saudi Arabia, and Venezuela block Tor traffic. Meanwhile, Tor isn’t only banned in China, but also illegal.
Moreover, keep in mind that while you may be using Tor in a country where no restrictions apply, your ISP and other third parties can still see that you are connected through the Tor browser. As a result, you may draw unwanted attention to your online activities.
Is Tor Safe to Use?
The Tor network is a free solution to a lot of online privacy problems. However, just like any other system, it has its vulnerabilities.
As we discussed above, if you’re not using an https connection, the exit node operator can see your traffic. The latter is in charge of decrypting your traffic, so if you’re not using a secure connection, your information will be exposed. And that’s not all, advanced hackers can target any node in an attempt to hijack data like system login information.
Furthermore, government agencies like the NSA use sophisticated and powerful attacks to monitor user traffic transmission between nodes and determine connection patterns. In fact, a lot of Tor nodes are actually owned by the NSA. Therefore, it is possible for third parties to collect user data and IP addresses.
The Onion Router also has a bad reputation as hackers and criminals use it to access the dark web. The latter is full of malware that could harm your device so be careful when you visit it. But because Tor is associated with the dark web, regular users will suffer the same scrutiny from government agencies.
How to Install and Use Tor Browser
The Tor browser is very similar to Mozilla Firefox. There are a few modifications here and there, but most of the code is similar. So if you’ve used Firefox, Tor won’t be new to you. And even if you’re not a firefox user, Tor is just like any other browser in terms of usability.
First, you must download the Tor Browser by visiting the Tor project website. You can also directly click this link and get the browser on your Windows, OS X, Linux, or Android device.
- Download Tor.
- Execute the file you downloaded to extract Tor Browser into a folder on your computer. You can choose any location on your device, with the default being your desktop.
- Once you select the location, click install and Tor does the rest.
And to start using Tor, follow the below steps:
- Open the Tor Browser file.
- Click Start Tor Browser.
- A new window will open asking you whether you’d like to connect or configure.

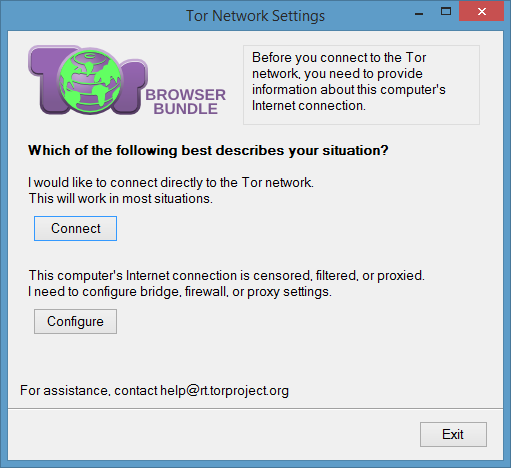
- Hit connect and a few seconds later a modified Firefox will open.
- You can now browse anonymously using Tor.
What Is Tor – Final Words
If you’re looking for online anonymity, the Tor Browser is more than a decent free solution. You can even add extra privacy by installing a premium VPN service. However, multiple traffic encryption and rerouting will consume your Internet connection and speeds will drop.
Either way, the Tor project enables access to valuable privacy tools such as the Tor Browser and the Tor Messenger. And these times, privacy is hard to come by.
Do you think the Tor network is reliable when it comes to privacy and anonymity? Let us know below.



