What Is PGP Encryption and How to Use It


- PGP encryption explained
- How does PGP work?
- PGP advantages and disadvantages
- PGP with VPN - Extra privacy
Pretty Good Privacy (PGP) is the oldest encryption algorithm for ciphering online email messages. It was released as a free-to-use security tool back in 1991 and is now a standard for email security. The cipher became popular because it allowed users to exchange encrypted messages over the Internet.
The PGP algorithm uses both symmetric and asymmetric encryption as well as public keys, enabling strangers to communicate safely when sending emails. Each public key is associated with a username and an email address, and each step uses a different algorithm.
The primary use of PGP is for encrypting communications, mostly texts, files, and emails. This trend leads to a flourishing market for email encryption services, which are forecast to triple in terms of revenue between 2015 and 2020, according to Statista data.
The PGP encryption system is one of the major players on the market for email encryption, following its acquisition by Symantec. It is now used to secure email messages, text documents, data files, and hard-disk partitions.
How Does PGP Encryption Work?
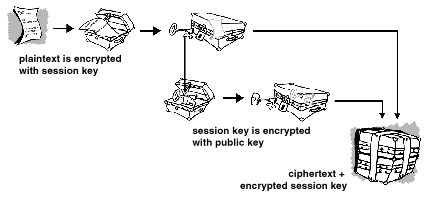
The message exchange logic of PGP is very simple. First, it compresses the plaintext before encrypting it to reduce data transmission time and disk space. Furthermore, data compression strengthens encryption security as most cryptanalysis methods target the plaintext to break the cipher. When PGP compresses the latter, it reduces such risks.
Second, Pretty Good Privacy creates a one-time secret key called a session key. It is a random number that comes from the movement of your mouse and keyboard strokes. The session key works with a secure encryption algorithm to cipher the plaintext and produce a ciphertext. Then, PGP will encrypt both the message and its session key with the recipient’s public key. Both keys are then sent to the receiver so that they can decrypt the text.
Here’s how the following illustration explains the process:

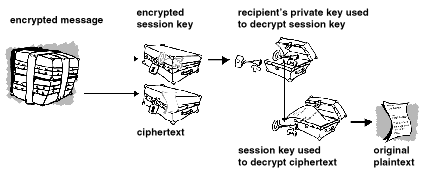
When the recipient receives the message, his or her private key will decrypt the session key, which in turn allows them to decipher the ciphertext and read the message.

PGP also involves message authentication and integrity checks. Digital signatures combine data derived from a sender’s message with the sender’s private PGP key to prove the authenticity of the user. In other words, it helps the recipient determine if the sender is who he claims to be. The unique digital signature also guarantees that the message has not been altered during transmission.
Another security feature of PGP is a requirement for distributing public keys in a way to produce an identity certificate that is very hard to forge. Since you have certificates for public keys, you can also guarantee that only the intended recipient will be able to read your messages.
Benefits of PGP Encryption
With PGP, you get the aforementioned message encryption that only you and the recipient can view and read. Furthermore, your messages will remain intact and the authenticity of the sender won’t be compromised.
The use of PGP for encrypting online communications also eliminates the risk of someone intercepting your sensitive messages or reading them by mistake. Only you and the holder of the respective public key can read the message. Even if your email message lands in the wrong mailbox, it stays private because the receiver does not have the proper key to decipher it.
Inexperienced users can also take advantage of PGP software as the application takes care of all the data encryption/decryption. All you need to do is learn how to use a slightly more advanced version of an email client.
Downsides of PGP Encryption
Lack of anonymity is probably the clearest disadvantage of PGP encryption. While your messages get the best cryptography standards, third parties can still trace them back to you and the recipient. If you want both privacy and anonymity, you must complement PGP with the best VPN service that hides and encrypts sensitive data.
While PGP apps are easy to learn, you have to get familiar with common practices to avoid costly mistakes. For example, PGP does not encrypt the subject line of your messages, so you should not enter any sensitive information there.
In any case, learning the basics of PGP is as easy as discovering any other software. And for extra privacy and anonymity, you can always install a VPN or use the Tor network.
PGP with VPN
VPNs, short for virtual private networks, are tools that maintain your online privacy. They send your traffic through their own servers instead of using the ones your Internet service provider uses. Then, they give you a different IP address that matches the location of the server you selected.
As you may know, the IP address that your ISP provides helps web services determine your approximate geographic location. Therefore, by switching your IP to a different country or region, websites won’t be able to track your actual location and will think that you’re someplace else. Furthermore, you’ll also be able to access geo-restricted streaming platforms like Netflix US and BBC iPlayer, not to mention bypass online censorship.
And most importantly, premium VPN brands use top encryption algorithms like the Advanced Encryption Standard with 256-bit keys. That means third parties won’t be able to monitor your Internet activities. Reputable VPNs also don’t collect sensitive data like IP addresses, browsing history, or the websites you visit. Instead, they eliminate such information from their servers.
Using PGP for Data Encryption
Users traditionally use the PGP system for encrypting messages. But organizations also take advantage of PGP’s abilities to encrypt data files.
After Symantec acquired PGP back in 2010, they developed a number of enterprise-grade solutions to encrypt files at scale with PGP encryption. Users can cipher files they share across networks, with solutions for full disk encryption on desktop and mobile devices as well.
In addition, there are PGP add-ons for popular email clients such as Apple Mail, Gmail, Outlook, and Thunderbird. PGP email applications are available for Android mobile users as well.
PGP Encryption – Final Words
In conclusion, PGP encrypts your messages and files but does not offer anonymity. Nonetheless, it should be part of a wider cyber-security strategy if you want to maintain total protection both online and offline.
For example, you can use a VPN to hide your online activities and physical location. Meanwhile, reputable antivirus programs and regular data backups protect you from malware. Having all three tools will significantly increase your Internet security and privacy.
Would you use a VPN with PGP for extra privacy? Let us know below.



