How a VPN Differs from a Proxy Server


- The difference between VPNs and proxy servers
- How proxy servers work
- How VPNs work
People around the world have growing concerns about how companies and governments treat their personal information and online activities. As a result, cybersecurity tools that can protect your Internet privacy and bypass web restrictions surged in the last few years.
Average Internet users have two options to get more online privacy and freedom: Using a proxy server or a virtual private network (VPN).
Both act as an intermediary between you and the websites you visit. Nonetheless, a proxy server markedly differs from a VPN. Actually, one of the few common features between a VPN and a proxy is that they both hide your real IP address and replace it with an IP that their servers provide.
How a Proxy Server Works
As I mentioned above, a proxy server acts as a middleman between your device and the websites you want to access. It handles your requests on your behalf, making it appear as if your traffic is coming from a different location. In other words, proxy servers don’t reveal the actual origin of the request.
So if, for example, you’re in San Francisco and you open the New York Times through a proxy server in Dublin, the website will think that you’re in Ireland. As a result, you won’t just protect your online location, but you’ll also be able to circumvent geo-restrictions that some sites impose.
And speaking of the New York Times, the news website and some other similar services allow you to access a limited number of articles per month. Once you exceed that number, you’ll have to pay to get the unlimited version. But when you use a proxy server, these websites won’t be able to track you using your IP address. Instead, they will think that you are a new visitor each time because proxy servers change your IP address.
How Proxy Servers Operate
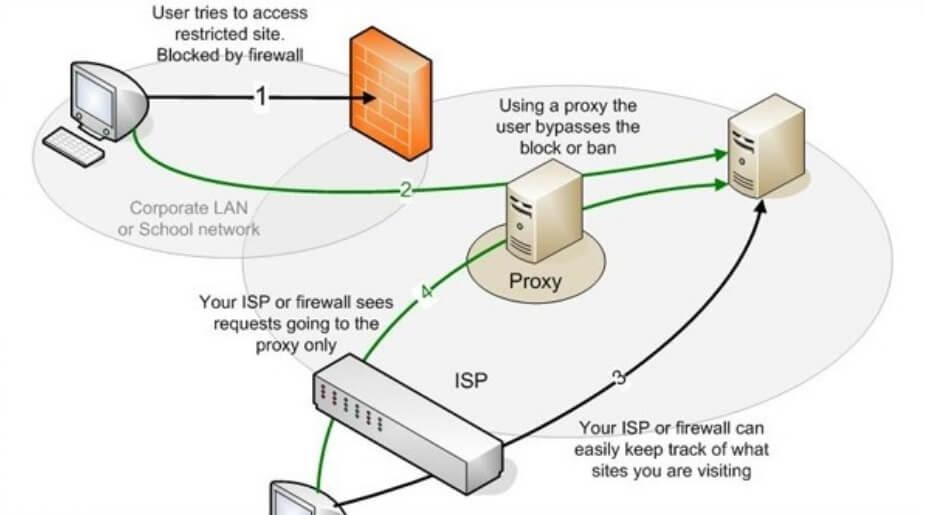

The problem with proxies is that they don’t encrypt your traffic, meaning government agencies, Internet service providers, and hackers can monitor your online activities. Furthermore, a proxy does not provide overall Internet connectivity protection for your device since it acts as an intermediary for a single application, usually a web browser, to connect to a website. Such an app-by-app approach does not provide wider protection for your online activities.
Among the most common proxy protocol types is the HTTP proxy, which is limited to processing web traffic only. In other words, you can mostly use this proxy to browse the Internet or exchange data with web-based apps.
Another popular proxy protocol is the SOCKS proxy. Unlike HTTP, It can handle any request that comes its way. That includes traffic for web servers, FTP servers, or BitTorrent clients. However, SOCKS proxies are slower than their HTTP counterparts as they pick up all sorts of traffic. Also, they don’t offer any encryption, just like HTTP.
Therefore, you should only use a proxy server when your only concern is to circumvent geo-blocked content. If you’re looking for online privacy and anonymity, these tools won’t provide it.
Are Free Proxies Safe?
Why pay for a service that you can get for free? A lot of users prefer not to pay for a proxy server, despite the huge risks that endanger their data. You see, you’re putting a lot of trust in proxy servers as you permit them to handle your web traffic.
That means they can monitor your online activities, including your browsing history and web destinations. They also collect your IP address, which reveals your location and digital identity. Furthermore, free proxy servers may contain malware, whether in their servers or through third-party ads.
And the thing about these free tools is that you don’t know who operates them. You could be using them to access geo-blocked websites like streaming platforms, but they will redirect you to shady websites to steal your sensitive data. That includes passwords to your banking account or credit card credentials.
Smart DNS Proxies
If you’re only looking to access geo-restricted streaming platforms, like Hulu or BBC Player, then you’re better off with a Smart DNS proxy. This tool only handles requests to specific websites, depending on its channel support list. It can bypass geo-blocks by just rerouting the URLs that expose your location, leaving the rest of your traffic intact.
However, they don’t hide your IP address nor encrypt your traffic. So if you’re looking for privacy, stick to a VPN service. Streaming fans can benefit the most from a Smart DNS as it allows them to stream their favorite shows from anywhere.
Unlocator, for example, can unblock more than 220 streaming platforms. Its channel support list features Hulu, Amazon Prime Video, HBO Now, Disney+, BBC iPlayer, ITV Hub, and ESPN+. It also offers a no-credit-card 7-day free trial, as well as a 30-day refund policy.
How to Set up a Proxy Server on Your Device
You can easily set up a proxy server on any device you want. For Windows, open settings, then click Network and Internet => Proxy => enable Use Setup Script => enter the script address => Save.
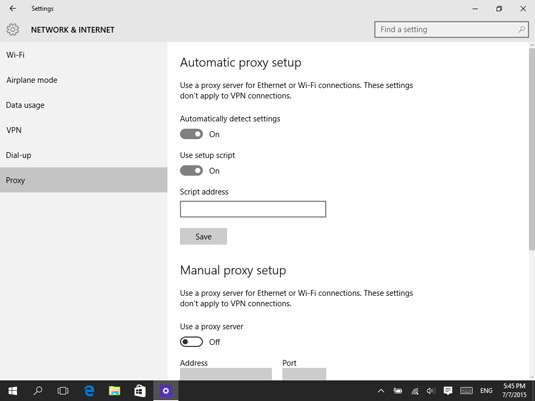

As for Mac, click on the Apple icon on the top left, followed by Systems and Preferences. Then, hit Network, followed by Advanced. After that, click the proxies tab and choose the protocol you want to configure.
How a VPN Service Works
Anything proxy servers can do, virtual private networks can do better. A VPN conceals your actual IP address and replaces it with a different one that its servers provide.
Additionally, VPNs offer more layers of privacy and security by rerouting all your traffic through its servers, not just at the application level. They also encrypt your connection, which makes it nearly impossible for snooping parties to decode your online activities.
How VPN Servers Operate
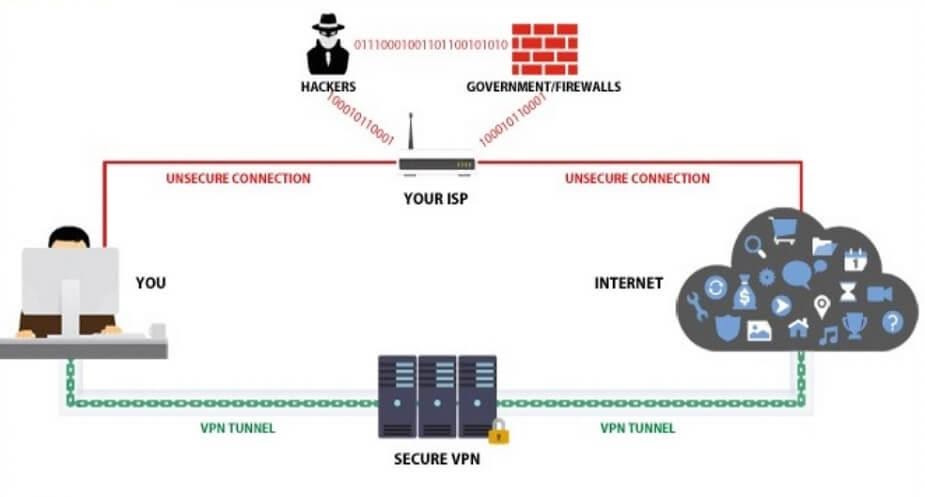

As a result, you can use a VPN to circumvent online geographic restrictions and avoid Internet censorship. Furthermore, most VPNs offer features such as the kill-switch, which disconnects you from the Internet in case the VPN connection drops. That means your traffic won’t leak to your ISP’s servers where anyone can see it.
VPNs also have a split tunneling option, allowing you to choose the apps you want to protect with a VPN, while the rest of your traffic intact. Virtual private networks are also excellent tools for P2P file-sharing as they protect users from legal action from copyright holders.
Actually, the two most important differences between a proxy server and a VPN are the encryption capability and the kill switch. Therefore, you should use a VPN service when you need more online privacy and security.
What about Free VPNs?
Even though VPNs have an edge over proxy servers in terms of privacy and security, free providers can actually endanger your anonymity. That’s because these brands will count on advertisements to generate money, which usually means collecting your sensitive data and selling it to third parties.
Furthermore, free VPNs sometimes don’t use encryption protocols, leaving your online activities out there for ISPs and government agencies to see. And just like proxy servers, some of them contain malware, whether through ads or in their software.
Therefore, stick to premium VPNs like ExpressVPN, BulletVPN, Unlocator VPN, and NordVPN.
How to Install a VPN on Your Device?
Unlike proxy servers, elite VPNs have dedicated apps for the majority of operating systems. So you won’t have to manually configure them on your smartphone, tablet, or laptop. However, if you’re going to use them on your router, Smart TV, or gaming consoles, then you’ll need to follow the setup guides on your VPN website.
- Sign up to a premium VPN service like the one I suggested above.
- Go to Google Play or the App Store to install the VPN on your device. The apps are compatible with Android, iOS, Mac, and Windows, while some brands have apps for Linux and Kindle Fire as well.
- Open the VPN app, sign in, then connect to any server.
- Enjoy the ultimate privacy and Internet freedom.
Final Words
Whether you will use a proxy or a VPN depends on your specific needs and preferences. You can even use a proxy and a VPN service simultaneously (although this option needs advanced user skills). However, you should note that VPNs can do everything proxy servers can do, but with more privacy and security.
Moreover, VPNs are much more efficient in unblocking restricted online material as they reroute your entire Internet traffic, change your IP address, and encrypt your data.
Which service do you think is better, a VPN or a proxy server? Leave your comments in the box below.




One Comment